High concentration of organic matter:
A large amount of organic waste will be produced in aquaculture water bodies, such as feed residues, excrement, etc. This organic matter accumulates in the water, resulting in a high concentration of organic matter in the wastewater.
High ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen content:
During the breeding process, the excreta of fish and other cultured organisms contain ammonia nitrogen, and the ammonia nitrogen in the culture water body needs to be effectively treated to prevent harmful effects on the cultured organisms.
Suspended solid matter:
Wastewater may contain a large amount of suspended solids, such as feed residues, algae, microorganisms, etc. These substances have a certain impact on water quality.
Microbial community:
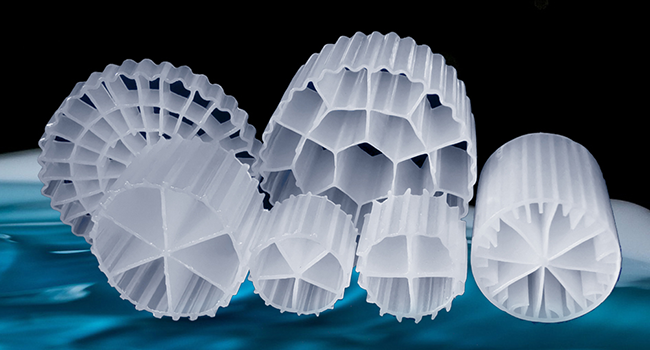
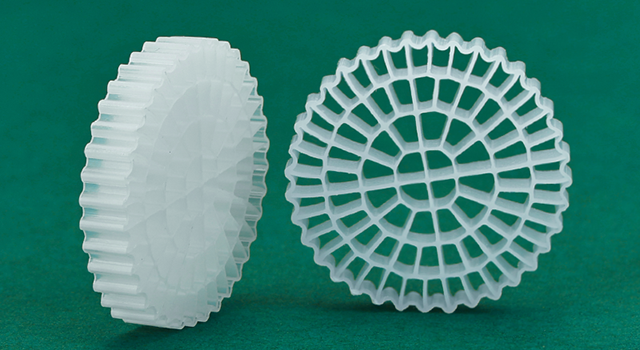
There are a large number of microorganisms in the circulating culture system, including beneficial biodegrading bacteria and other microorganisms. These microorganisms play an important role in water quality stability and wastewater treatment.