What is Mbbr
What is MBBR?
The MBBR (Moving-Bed Biofilm Reactor) process is an advanced wastewater treatment technology that has gained considerable attention in recent years. It uses suspended carriers to provide a surface for microorganisms to attach, addressing the issues of periodic backwashing and complex maintenance required by traditional reactors. This makes it an efficient and simple treatment method. This article provides a detailed introduction and explanation of MBBR.
1.What is MBBR?
MBBR is a new type of biofilm reactor developed to overcome the operational complexity of traditional fixed-bed and fluidized-bed reactors. It provides a surface for microorganisms to attach by using constantly moving suspended carriers, reducing the need for common maintenance operations like backwashing and cleaning filter media.
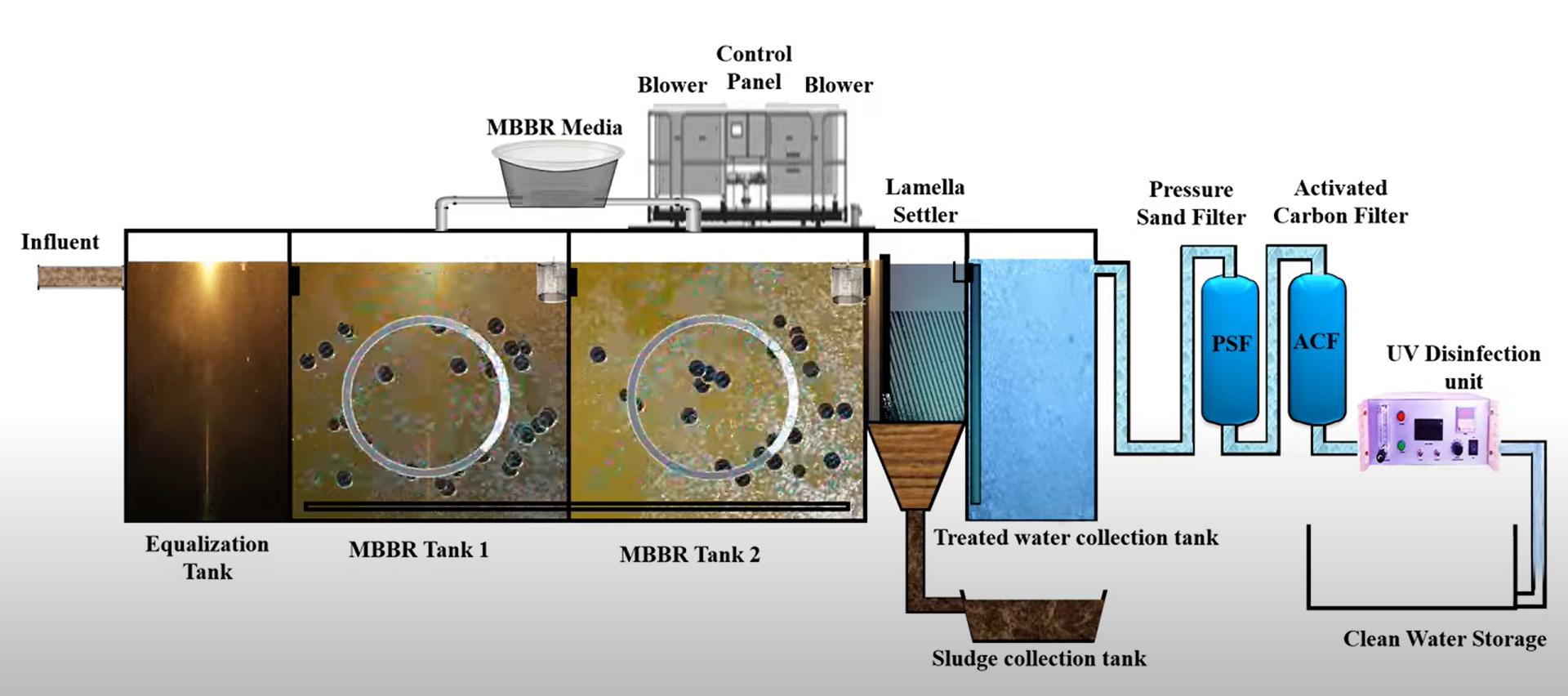
2. Principles and Characteristics of MBBR
(1) MBBR Principles:
In an MBBR(Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) reactor, a certain number of suspended carriers are added, and microorganisms attach to these carriers to form biofilms. Organic matter in the wastewater diffuses into the biofilm and is degraded by the microorganisms. The carriers remain in motion due to aeration or stirring, enhancing the contact between microorganisms and pollutants. The MBBR process does not require sludge recirculation, has a simple structure, high treatment efficiency, and is suitable for various types of wastewater.
The MBBR process combines the advantages of traditional fluidized-bed and biological contact oxidation methods, making it a new, highly efficient wastewater treatment method. The carriers remain fluidized due to aeration and water flow, forming suspended activated sludge and attached biofilms, utilizing the entire reactor space. These moving carriers frequently come into contact with the wastewater, earning the nickname "moving biofilm."
(2) Advantages of MBBR

Carrier Characteristics:
The carriers are typically made from materials like polyethylene, polyurethane foam, polypropylene, or their modified versions, with a density close to water. They are usually cylindrical or spherical in shape, making it easier for microorganisms to form biofilms without agglomerating or clogging. The Aquasust MBBR78S carriers are S-shaped, offering better mobility and preventing attachment to tank walls.
Treatment Capacity:
The carriers create aerobic, anoxic, and anaerobic environments, allowing both nitrification and denitrification reactions to occur in the same reactor, resulting in efficient ammonia nitrogen removal. The sludge concentration is generally 5 to 10 times that of the conventional activated sludge process, with a maximum concentration of 30-40g/L, significantly improving the efficiency of organic matter removal while maintaining strong resistance to shock loads.
Ease of Maintenance:
The MBBR process does not require carrier support structures, and the aeration system is easy to maintain. Additionally, the system has a small footprint, reducing both construction and operational costs.
3. Conclusion:
By using innovative suspended carriers and biofilm reactor design, the MBBR process effectively improves wastewater treatment efficiency while reducing maintenance and operational complexity. It has thus become a popular choice in the wastewater treatment field.





